Windows 10 introduces Cortana and various features to streamline tasks. Understanding these tools and their tricks maximizes efficiency. Below, discover essential and advanced search tips & tricks for Windows 10 to enhance data retrieval on your #Win10 PC.
Utilize Cortana
Cortana, Microsoft’s counterpart to Apple’s Siri, offers enhanced search capabilities on Windows 10. Utilize Cortana for natural and voice-based searches, locally and online. It’s a standout feature of Windows 10, elevating search functionality beyond basic queries.
- Click the search button in the Taskbar
- Type or speak your query to see results
- Select any filters (icons in the top bar) to check specific results; for example, the Settings filter shows settings/configuration items only, while the Web filter displays web results instead of local findings
Search from the Search Box
The Search box, located at the top-right of the File Explorer, is the easiest method to search for files or folders within the current directory. It looks up data in the current opened directory, whether it’s the computer, individual drive, or a particular folder.
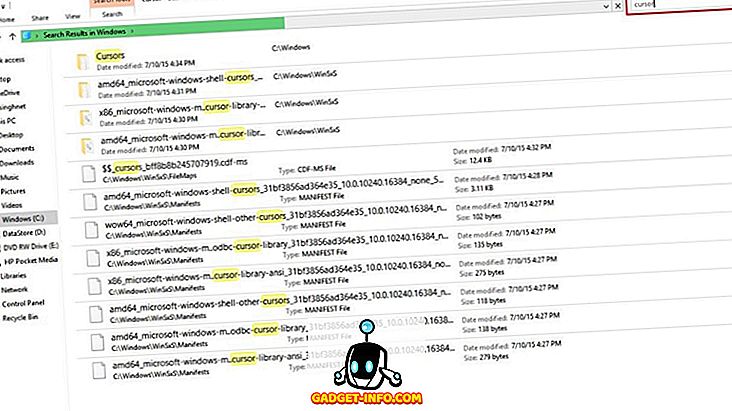
With thousands of files on your PC, you might forget their locations, hence this search box helps when you’re in need. For instance, if you forgot the location of a file named ‘Market Report.docx’, simply type ‘market’ or ‘report’ in the search box and hit Enter, Windows 10 will instantly display all files with similar names.
Use Wildcards
Wildcards are fillers to guess names for searching information when you aren’t sure of the keyword. It helps retrieve results by substituting the wildcard with possible combinations of letters and searching those names.
- * (asterisk): None, one, or more characters replace it. For instance, typing ‘eas*‘ searches for names starting with ‘eas‘ and may end with any additional characters, yielding results such as ‘eas’, ‘easy’, ‘easier’, etc.
- ? (question mark): Only one character replaces it (not none). For example, typing ‘ad?pt‘ can display names like ‘adapt’, ‘adopt’, ‘adept’, etc.
- # (pound or hashtag): A set of numeric digits replaces it. For instance, typing ‘2#4‘ displays ‘204’, ‘214’, and any name with numbers between 2 and 4.
- name (File Name): Incorporate part or full name into your search to locate files by name. For instance, for a file named ‘May Worksheet’, enter ‘May’ or ‘work’ and similar terms. Additionally, utilize key/value pairs like ‘name: May’, ‘name: work’, etc.
- kind (File Kind): Specify the type of file you seek, such as ‘document’, ‘audio’, etc. Similarly, employ key/value pairs like ‘kind: document’, ‘kind: other’, etc.
- type: File Type/Extension: Include format name like TXT, DOCX, JPG, BMP, etc. One can also use key/value pair such as ‘type: EXE’, ‘type: TXT’, etc.
- tags: Tags: Include any tag or keyword used to describe file(s). One can also use key/value pair such as ‘tags: project’, ‘tags: school’, etc.
- author: Author: Include author’s name to search for files by creator(s). One can also use key/value pair, for example, ‘author: john’, ‘author: lina’, etc.
- AND: Use ‘AND’ to search for both terms. For example, ‘word AND pad’ searches for files containing both words and yields results such as ‘wordpad.exe’, ‘word notepad.txt’, etc.
- OR: Include ‘OR’ to search for any of the terms. For instance, ‘word OR pad’ searches for files containing either word and yields results like ‘word.exe’, ‘notepad.txt’, etc.
- Quotes: Include your query under double quotes “” to search for exact phrases or filenames, like ‘“India Gate”’ (including double quotes and excluding single quotes) shows files with the exact name ‘India Gate’.
- Parentheses: Include your query under parentheses () to search for all of those words (but even if those are present in any order). For example, ‘(cricket football hockey)’ search gives ‘cricket hockey football.txt’, ‘hockey football cricket.docx’, etc.
- On the search results screen, click ‘View’ and select ‘Details’
- Click ‘View’, then ‘Sort by’
- Choose the sorting field and order (ascending/descending)
- Click ‘View’, then ‘Group by’
- Choose the grouping field
- Hover over the column, click the down-arrow icon
- Choose filter values
- Use the Search Box in File Explorer
- Access the Search (Search Tools) ribbon
- Adjust available options/preferences
- Search results update as options are selected
- Perform a search using the Search Box in File Explorer
- Access the Search (Search Tools) ribbon
- Set your query preferences
- Finalize and test your search query, then click ‘Save search’
- Enter a name and location, then click Save
Optimizing File Properties
File Properties encompass the metadata or details regarding the file(s), such as creation date, file type, author (or creator), etc. These details aid in efficient file and folder searches, providing more information than solely filenames.
Use Boolean Filters
Boolean filters enable advanced searches by combining search terms or phrases. Various boolean operators are available as described below. Ensure you type the filters in capital letters when performing such searches.
Example search queries with explanations are provided below:
NOT: Include ‘NOT’ to avoid that term. For example, ‘NOT pad’ searches for files not having this word and results in ‘word.exe’, ‘word note.txt’, etc.
Refining Editorial Efficiency
In File Explorer’s Details view, file list headings are visible, even on search results screens. Leveraging these headings and a few tricks, one can efficiently locate files or information. For instance, if you’ve searched for ‘travel*’, and you’re presented with a list of travel invoices, simply sort the list by date created or modified in descending order to quickly find the latest file you need.
Refine Your Search Results Efficiently
To sort, follow these steps:
Utilize Advanced Search Tools
Advanced Search tools offer a range of search options to meet all your search needs – providing all possible advanced options on one screen. It’s used to search for files and folders with varying levels of information available, such as file location, tags, size, date, and properties, among others. With this tool, there’s no need to remember search operators. Additionally, it allows you to view recent searches and search using file properties.
Save Your Search Query
Windows 10, with its miraculous features, lets one save searches or search queries for future use efficiently. There may be scenarios where forming cumbersome queries becomes necessary for advanced searches. In such cases, the search save option proves invaluable.
To save your search query, follow these steps:
That’s all about search tips and tricks for Windows 10. Do you have any more to share? Let us know in the comments section.

Pritam Chopra is a seasoned IT professional and a passionate blogger hailing from the dynamic realm of technology. With an insatiable curiosity for all things tech-related, Pritam has dedicated himself to exploring and unraveling the intricacies of the digital world.