A plethora of devices, from smartphones to VR headsets and security cameras, swarm telecom networks simultaneously. This surge translates to escalating data traffic, necessitating enhanced bandwidth. Ultimately, what we crave is swift data transmission, right? Huawei, the Chinese telecom leader, anticipates a seven-fold surge in global mobile data traffic by 2021 compared to 2016. Moreover, it predicts that individual data consumption will average 15GB monthly in the next five years. While countries like India are still embracing 4G LTE, global telecom operators are delving into sophisticated technologies like Massive MIMO (Multiple Input, Multiple Output). This intelligent antenna system serves as the cornerstone of 5G cellular technology, promising amplified signal strength, user capacity, and data speeds. Though still in its infancy, Massive MIMO is poised for rapid integration. Curious about Massive MIMO? Here’s your comprehensive guide:
Understanding Massive MIMO’s Role in 5G
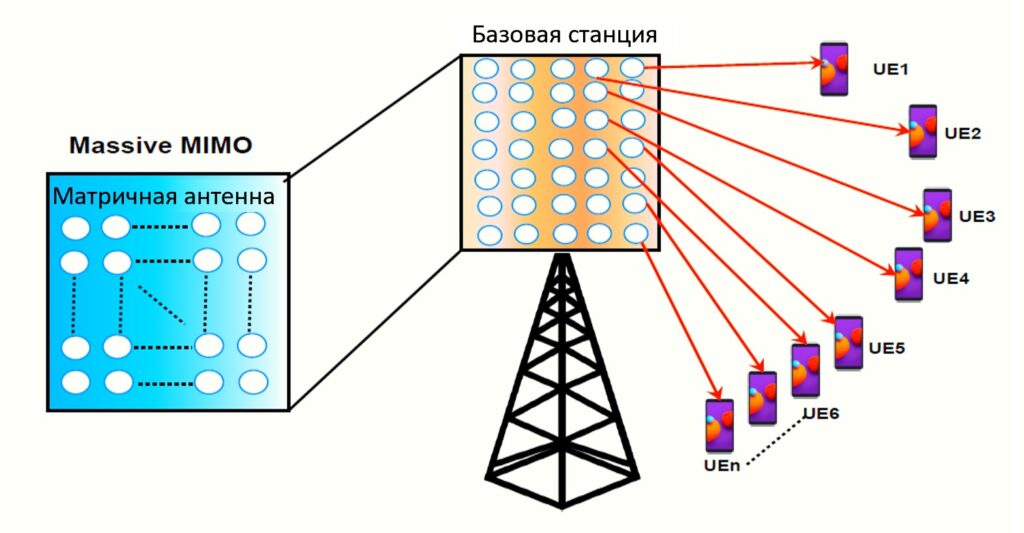
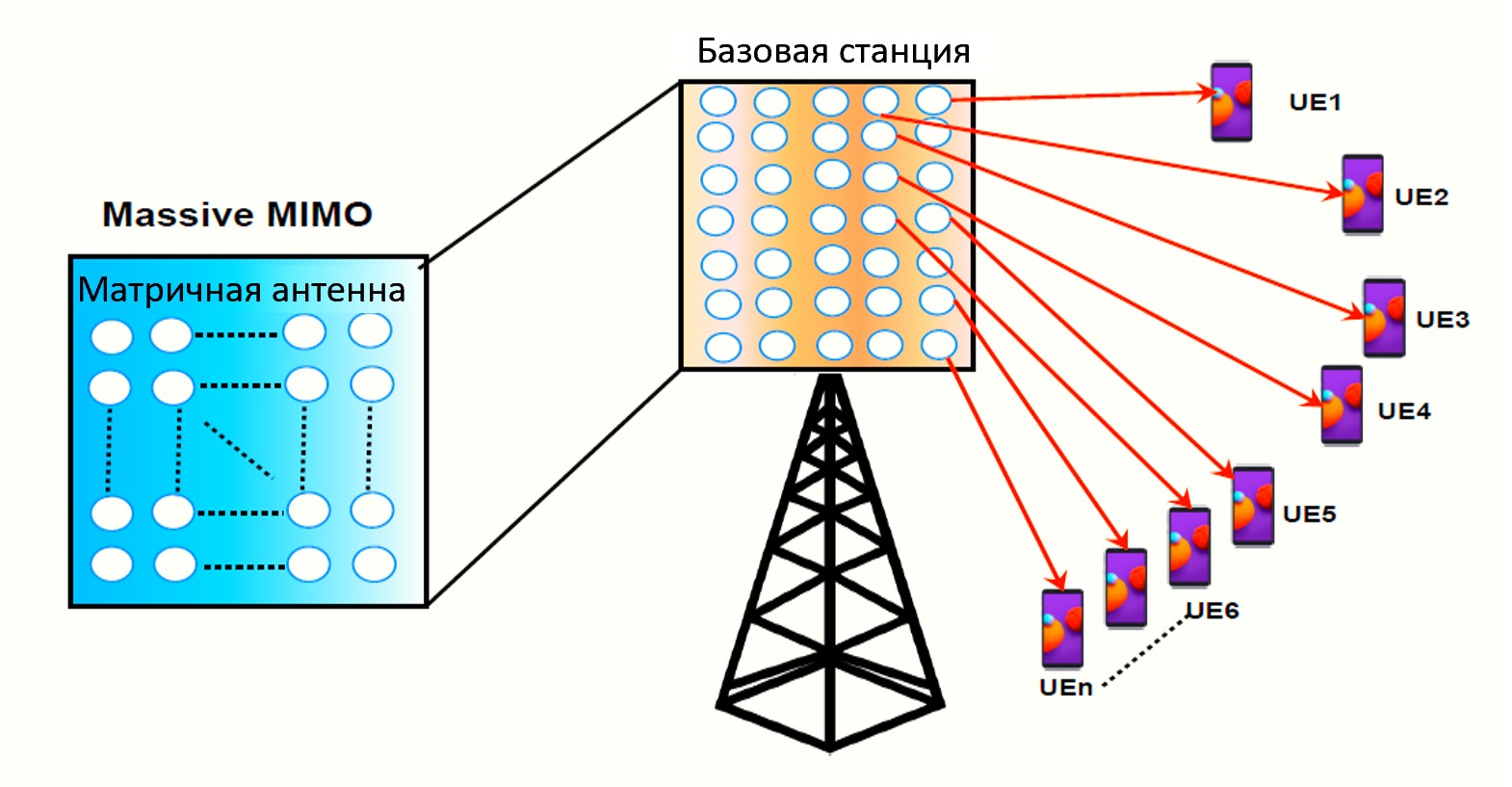
Massive MIMO (Multiple Input, Multiple Output), also referred to as Large-Scale Antenna Systems, underpins the advancement of wireless communication. This technology is poised to significantly benefit by supporting more mobile users and delivering faster, more reliable network services over time.
Presently, most 4G LTE network infrastructures only support up to 8 antennas (transmitter + receiver) at the base station, which fails to meet the increasing demands of mobile users. This limitation results in constrained bandwidth, impacting data speed and the number of users able to connect to the station.
Here’s where MIMO comes in, enabling simultaneous data exchange over the same radio channel using two or more transmitters and receivers. This technology has been implemented in advanced 4G network stations as 4 x 4 MIMO and is under exploration by operators in India. (Image courtesy: National Instruments)
Expanding the concept to accommodate nearly 100 antennas in a single array at the base station (cellular tower) forms the basis for upcoming 5G networks. The increase in antennas results in more transmitters/receivers, increasing signal paths and enhancing performance in data speeds and link reliability. Massive MIMO can improve speeds up to four times and expand network capacity significantly.
This enables operators to serve a larger number of mobile devices in an area by deploying Massive MIMO technology. Additionally, operators can scale by adding more antennas to increase signal paths and efficiency without affecting the existing spectrum.
Advantages of Massive MIMO Compared to Current 4G Networks
Utilizing a greater number of input and output antennas in Massive MIMO (5G) systems significantly enhances coverage and data speeds for telecom operators. This improvement stems from heightened spectral and energy efficiency, bolstered by extensive multiplexing and antenna array gain. Here are the key benefits of Massive MIMO (M-MIMO) antenna systems over existing 4G systems:
1. Enhanced Coverage and Speed
Massive MIMO technology, potentially in conjunction with higher frequency spectrums, enables telecom companies to serve a broader range of devices in the future. Moreover, indoor signal strength becomes exceptionally robust.
Massive MIMO systems’ beam-forming capabilities rapidly extend high-speed coverage to rural areas. Direct line of sight enhances speeds, especially with higher frequencies.
Upgrading aims to increase data speed, with experts anticipating minimum speeds of 1 Gbps, reaching up to 10 Gbps. This was demonstrated in Gigabit LTE demos by Chinese networking giant ZTE at CES earlier this year.
2. Low Infrastructure and Component Costs
As global telecom giants steadily upgrade their infrastructure to support high-speed 4G networks (with pre-5G speeds), complete upgradation to 5G would be smooth. Existing 4G systems already employ MIMO techniques, which will scale with plausible 5G technology.
The new Massive MIMO antenna systems will not only have a large number of antennas but also be scalable. Telecom giants can easily add new antennas to this system to augment existing speeds and user base. Additionally, the large number of antennas will create a robust network, unaffected by individual antenna failures.
3. Time-constricted Connections Support
Massive MIMO-enabled 5G networks enhance coverage and data speed while reducing signal travel time, known as latency. Upcoming 5G networks will further reduce latency, facilitating VR/AR, self-driving, and other AI or ML-controlled services.
Challenges in Massive MIMO Antenna Deployment
Researchers have experimented with Massive MIMO antenna tests for years, but market-available systems still lack antennas desired by telecom companies for 5G networks. Limitations in technology implementation pose challenges to widespread deployment. Here are the challenges:

1. Signal Processing Complexity
Setting up Massive MIMO base stations faces a significant challenge: the increased number of antennas and frequencies at one location raises interference risks. This can be addressed by using a broader spectrum and faultless precision technology, reducing inter-site channel interference. While more antennas increase complexity, they also enhance network resilience.
2. Spectrum Constraints
Frequencies are allocated by governing bodies, and telecom operators must bid for their desired section of the spectrum.
Technology giants and telecom operators collaborate to boost signal gain through multiple antennas (MIMO), focusing radio signals in narrow directional beams without increasing transmission power. Samsung R&D and Huawei have achieved success in experiments, but these beams are highly sensitive to alignment changes.
Ongoing Research and Deployment of Massive MIMO Networks
This network system is not merely a prototype but has already been implemented on a smaller scale in the existing 4G scenario. Huawei has partnered with local telecom operators such as China Mobile and Japan’s SoftBank for over a couple of years to commercially experiment with its Massive MIMO setups.
Following extensive experimentation, SoftBank has emerged as the pioneering telecom operator to unveil its commercial Massive MIMO network by late 2016. Concurrently, other major operators, including China Mobile, Vodafone, and T-Mobile, have initiated the deployment of this technology to a limited user base within their respective regions.
If you’re wondering whether our current smartphones will be compatible with these Massive MIMO networks, the simple answer is mostly affirmative. A considerable number of existing devices are equipped to leverage 4G MIMO networks, delivering Gigabit speeds seamlessly.
India’s Inaugural 5G-capable Deployments
While global telecom players, along with hardware giants, have experimented with Massive MIMO on their networks, India has recently joined the 5G drive with its first such network.
Airtel, India’s leading telecom giant, made headlines by announcing its achievement. The rollout of India’s first M-MIMO (Massive Multiple-Input Multiple-Output) technology has commenced in Bengaluru and Kolkata. The trial is expected to expand to other parts of the country soon.
Airtel deployed 5G technology as part of their network transformation, Project Leap, expecting Massive MIMO to boost capacity sevenfold using existing spectrum, also doubling speeds on current 4G.
ZTE joins pre-5G Massive MIMO trials with Vodafone and Reliance Jio. Huawei leads Airtel’s deployment in the country, as per official statement.
Viewed from the current state of the telecom industry in India, this represents telecom giants’ endeavor to retain dominance. Recently startled by Reliance Jio, their fiercest new competitor, they’ve been swiftly overtaken by its 4G LTE network rollout within a year.
Anticipated Nationwide Deployment
The 3G network technology debuted in October 2001, while 4G LTE saw widespread adoption around 2011. Speculation suggests ongoing Massive MIMO efforts will bear fruit by decade’s end. Pre-5G implementations of the technology may emerge in the next few years, both for consumers and operators. The audience at the 2018 Winter Olympics and the FIFA 2018 World Cup could witness this innovation firsthand. Chipmaker Qualcomm plans to release 5G-compatible (Gigabit) devices around the same time.
Despite the prolonged rollout of 4G LTE services in India, the country’s telecom giants are now eager to embrace the latest technologies due to fierce competition and consolidation.
Massive MIMO: The 5G Technological Race
Massive MIMO developments highlight India’s emergence as a technological powerhouse. The government is spearheading efforts to propel cellular technology forward.
Establishing a high-level forum, the government is evaluating the current scenario and approving action plans for 5G rollout. With a ₹500 crore allocation for 5G research and development, India joins global leaders in technological advancement. The definition of a true “5G” network remains elusive for now, necessitating vigilance in the years ahead.

Pritam Chopra is a seasoned IT professional and a passionate blogger hailing from the dynamic realm of technology. With an insatiable curiosity for all things tech-related, Pritam has dedicated himself to exploring and unraveling the intricacies of the digital world.