Commands wield immense power within the Linux terminal. However, retyping lengthy commands multiple times can be cumbersome. Thus, we present methods to efficiently view and manage your command history.
Viewing Command History
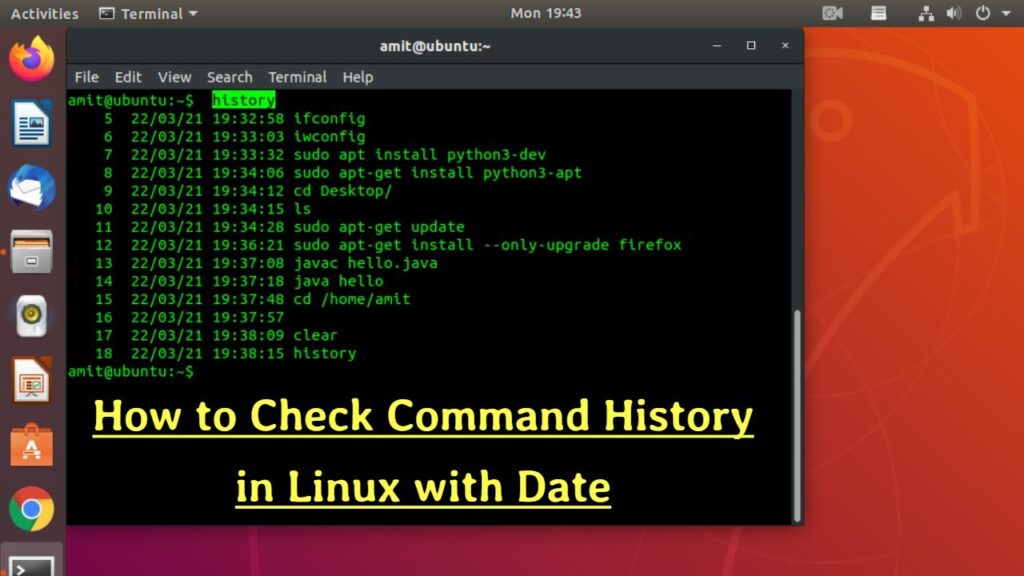
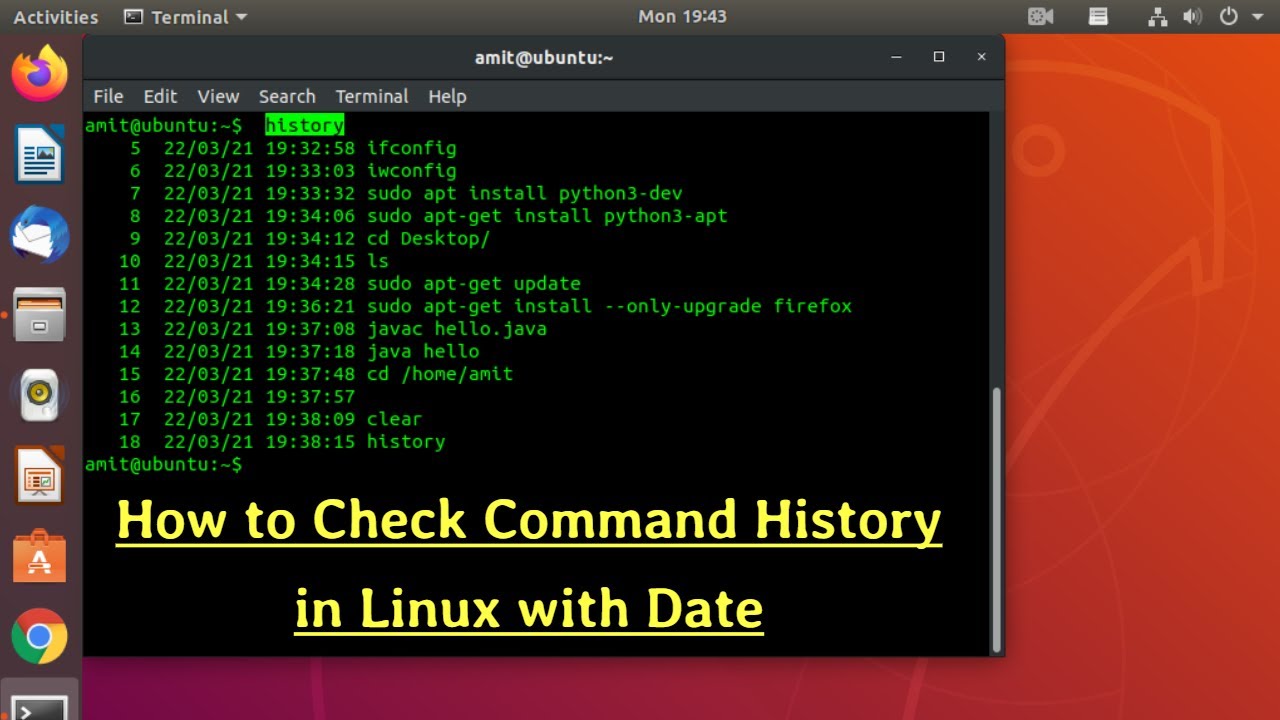
To review previously executed commands in Linux, utilize the straightforward history command:
history
Options to accompany the history command include:
| Options | Description |
|---|---|
| -c | Clears command history for the current session |
| -w | writes command history to a file |
| -r | reloads command history from the history file |
| -n | Limits output number of recent commands |
Run the history command to see the list of all previously executed commands in Linux terminal:
In addition to viewing command history, you can also manage it by modifying a previously executed command, reverse searching the history, or deleting it altogether.
Modify a Previously Executed Linux Command
Every executed command is stored in the command history. To modify or reuse a command, follow these steps:
Command History Expansion
- !! – Inserts the last command into the shell prompt.
- !n – Inserts the nth command into the shell prompt.
- ! – Refers to the most recently executed command.
- !?pattern – Refers to the most recent command containing “pattern”.
Reverse Command Search
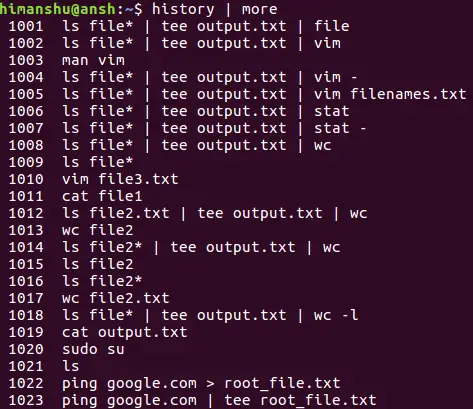
Sometimes scrolling through thousands of commands to find one is impractical. Instead, use the reverse command search with “CTRL + r”. This opens a new prompt. Type the desired command, and the previously executed one will appear. Press enter to execute.
Clearing Command History in Linux
To clear the entire command history, use the -c flag with the history command.
history -cModifying Command History Constraints in Linux
Command history in Linux is saved based on constraints, stored as system environment variables. Modify them like user-defined environment variables.
Limiting Stored Commands
To restrict command storage in history, set HISTSIZE using:
export HISTSIZE=
For instance, to retain solely the last 1000 commands:
export HISTSIZE=1000Excluding Specific Commands
To prevent specific commands from being saved in history, employ HISTIGNORE:
export HISTIGNORE=
For example, to exclude “ls,” “cd,” and “exit” commands:
export HISTIGNORE='ls:cd:exit'
Pritam Chopra is a seasoned IT professional and a passionate blogger hailing from the dynamic realm of technology. With an insatiable curiosity for all things tech-related, Pritam has dedicated himself to exploring and unraveling the intricacies of the digital world.